보다 선명한 태양 이미지에서의 태양 플레어
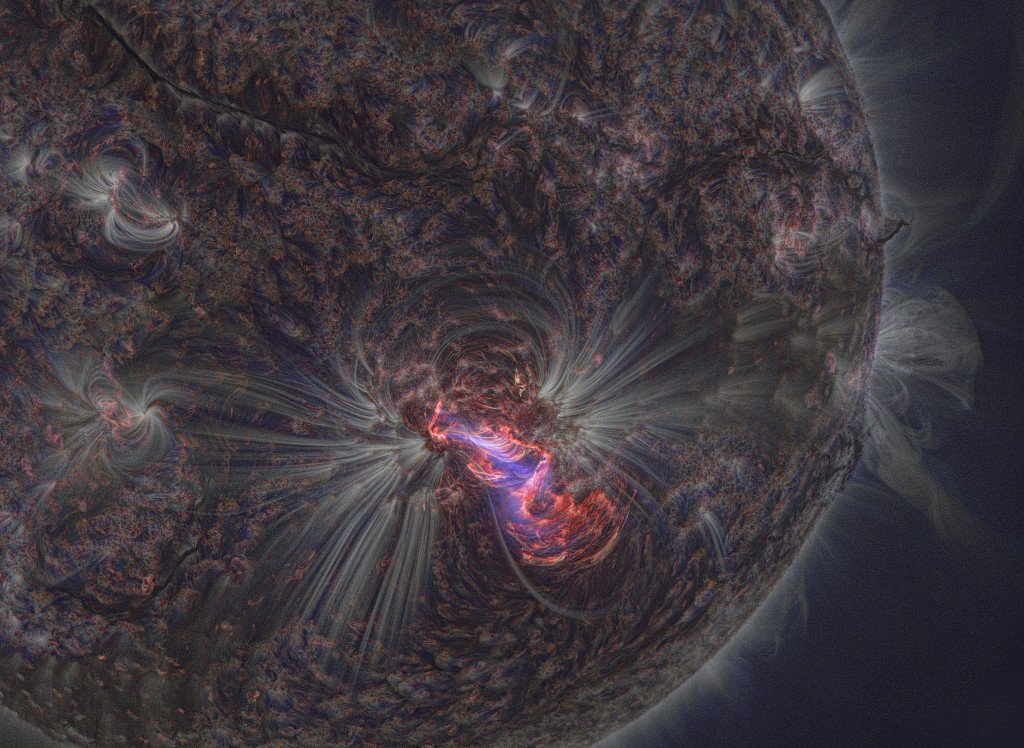
태양 활동영역 AR2192는 지난 24년 동안 기록된 흑점군 중에 가장 큰 것으로 기록되어 있습니다. 지난 시월 말 경, 지구를 향한 태양 면에서 사라지기 전에, 이 활동영역에서 탄성이 나올 만큼 강력한 X급 플레어가 6 개나 일어났습니다. 그 중 가장 강력한 플레어가 지구 궤도를 돌고 있는 태양역학천문대(Solar Dynamics Observatory)에서 10월 24일에 이 놀라운 화면 속에 잡혔습니다. 이 사진은 극자외선 영역의 서로 다른 세 파장의 빛을 이용하여 만들어진 합성이미지입니다. 파란색은 193Å, 하얀색은 171Å, 빨간색은 304Å의 빛을 나타냅니다. 높은 차수로 이온화된 철과 헬륨 원자의 방출선은 태양 바깥 쪽 채층과 코로나를 통과하며 루프형태를 가진 자기력선의 자취를 나타내줍니다. 그리고 그 아래, 보다 차가운 태양의 광구는 온도가 낮기 때문에 극자외선 영역에서 어둡게 나타납니다. 유난히 세밀한 모습을 보여주는 이 합성 이미지는 새로운 수학적 알고리즘, NAFE로 처리된 것입니다. NAFE는 극자외선 이미지 자료에서 나타나는 잡음과 밝기에 적응하여, 안정적으로 작은 세부구조를 보기위해 믿을 수 있을 만큼 확대하는 방법을 채택한 것입니다.
원문출처: http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap141122.html
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit: Solar Dynamics Observatory/AIA, NASA
Processing: NAFE by Miloslav Druckmuller (Brno University of Technology)
Explanation: Solar active region AR2192 was the largest recorded sunspot group of the last 24 years. Before rotating off the Earth-facing side of the Sun at the end of October, it produced a whopping six energetic X-class flares. Its most intense flare was captured on October 24 in this stunning view from the orbiting Solar Dynamics Observatory. The scene is a color combination of images made at three different wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light; 193 angstroms shown in blue, 171 angstroms in white, and 304 angstroms in red. The emission, from highly ionized Iron and Helium atoms, traces magnetic field lines looping through the hot plasma of the Sun's outer chromosphere and corona. Beneath, the cooler solar photosphere appears dark at extreme ultraviolet wavelengths. The exceptionally sharp composite image has been processed with a new mathematical algorithm (NAFE) that adapts to noise and brightness in extreme ultraviolet image data to reliably enhance small details.
'국문 APOD > 2014' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [APOD] 타이탄 위를 날다.(2014.11.24.) (0) | 2014.11.24 |
|---|---|
| [APOD] 켄자스 하늘의 토네이도와 무지개(2014.11.23.) (0) | 2014.11.23 |
| [APOD] M1 : 게성운 (2014.11.21.) (0) | 2014.11.21 |
| [APOD] LND 988 : 백조자리의 암흑성운(2014.11.20.) (0) | 2014.11.20 |
| [APOD] 밝은 나선은하 M81(2014.11.19.) (0) | 2014.11.19 |